1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
history = model.fit(X_train,y_train,validation_split=0.1, epochs =12, verbose=1, batch_size=32,
callbacks=[tensorboard,checkpoint,reduce_lr])
filterwarnings('ignore')
epochs = [i for i in range(12)]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(14,7))
train_acc = history.history['accuracy']
train_loss = history.history['loss']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
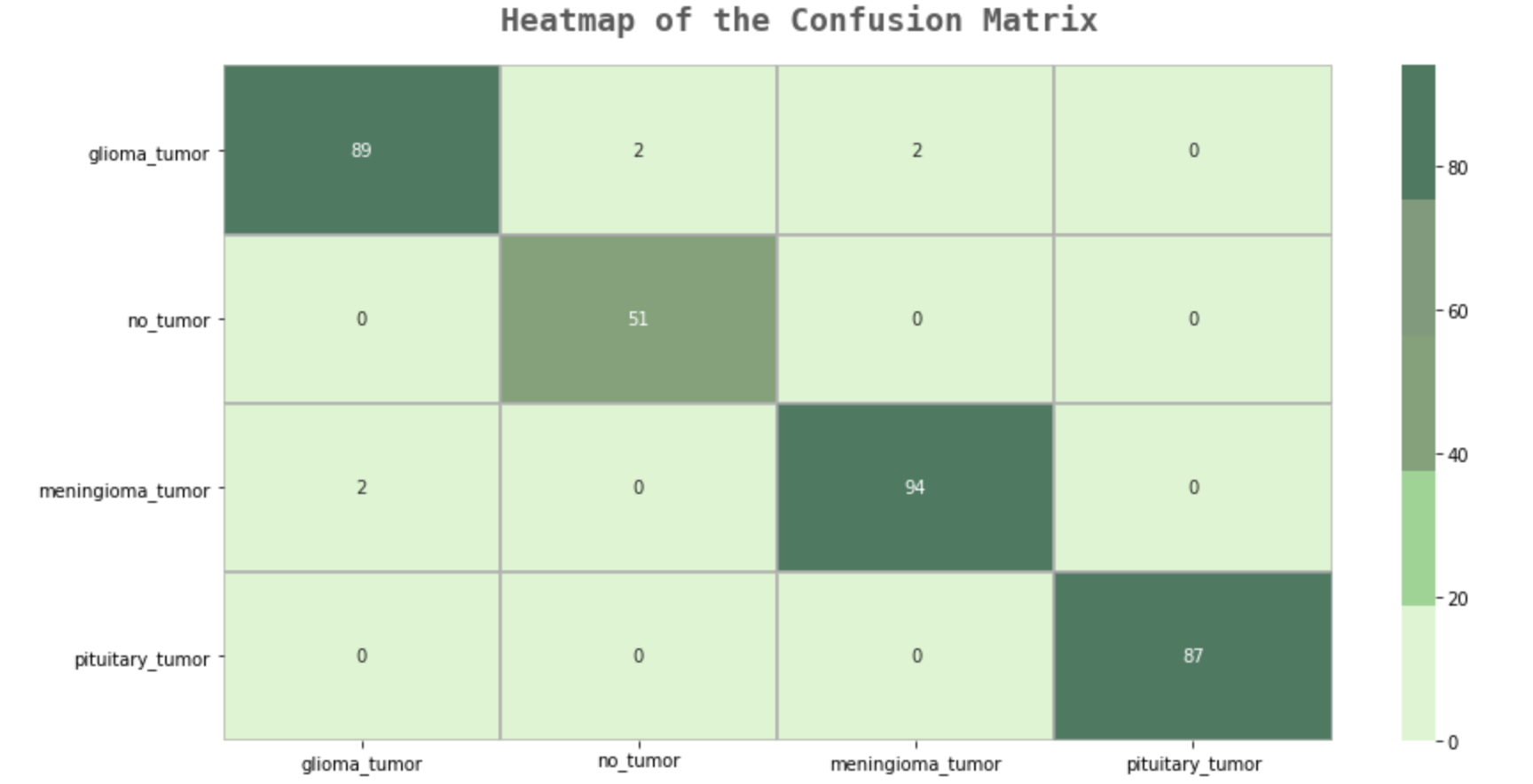
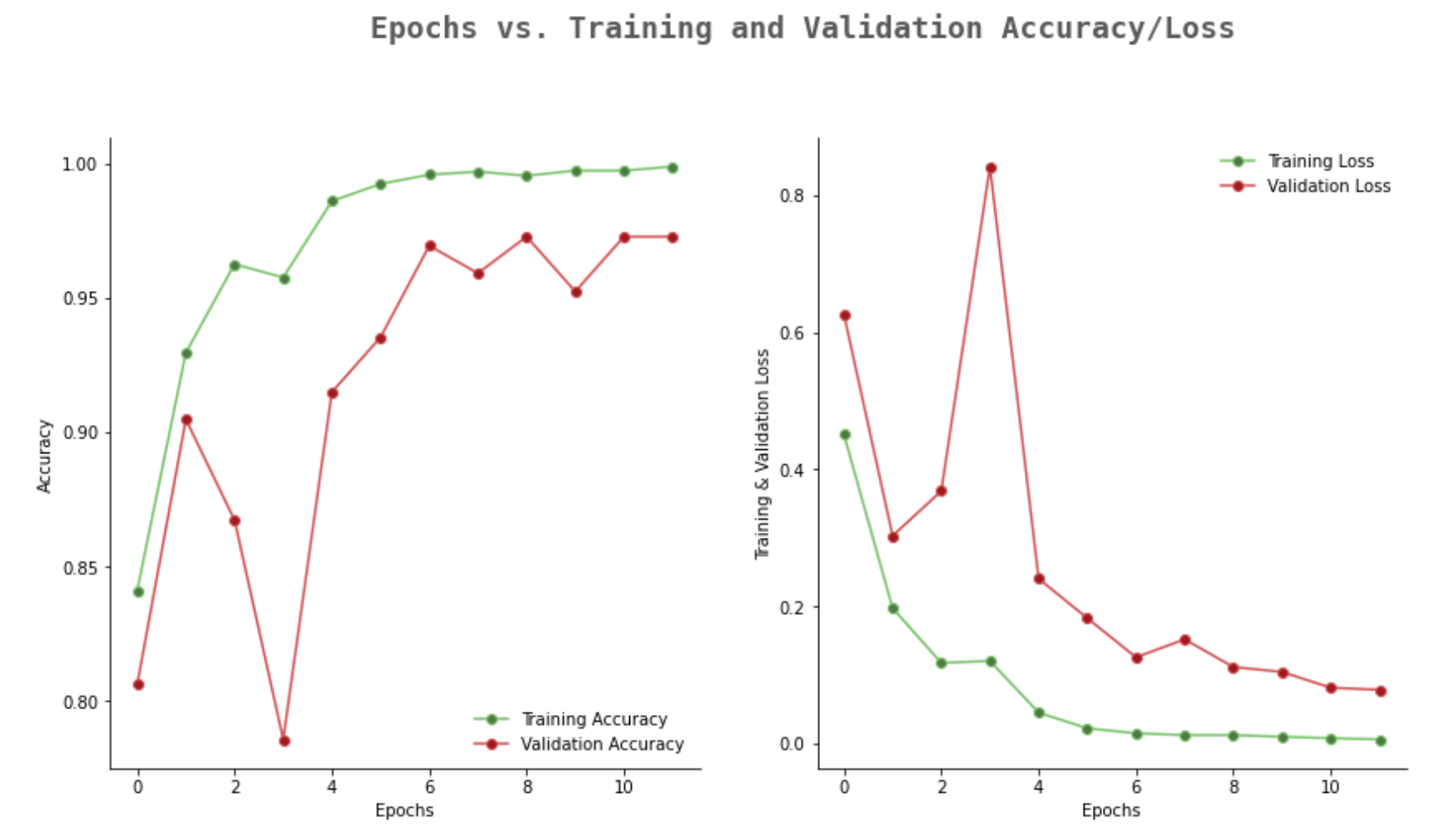
fig.text(s='Epochs vs. Training and Validation Accuracy/Loss',size=18,fontweight='bold',
fontname='monospace',color=colors_dark[1],y=1,x=0.28,alpha=0.8)
sns.despine()
ax[0].plot(epochs, train_acc, marker='o',markerfacecolor=colors_green[2],color=colors_green[3],
label = 'Training Accuracy')
ax[0].plot(epochs, val_acc, marker='o',markerfacecolor=colors_red[2],color=colors_red[3],
label = 'Validation Accuracy')
ax[0].legend(frameon=False)
ax[0].set_xlabel('Epochs')
ax[0].set_ylabel('Accuracy')
sns.despine()
ax[1].plot(epochs, train_loss, marker='o',markerfacecolor=colors_green[2],color=colors_green[3],
label ='Training Loss')
ax[1].plot(epochs, val_loss, marker='o',markerfacecolor=colors_red[2],color=colors_red[3],
label = 'Validation Loss')
ax[1].legend(frameon=False)
ax[1].set_xlabel('Epochs')
ax[1].set_ylabel('Training & Validation Loss')
fig.show()
|
![]()